As an Oracle DBA, you must understand the concepts
of Oracle architecture clearly. It is a basic step ormain point that you
need before you go to manage your database. By this article, I will try to
share my knowledge about it. Hope it can be useful for you.
What is An Oracle Database?
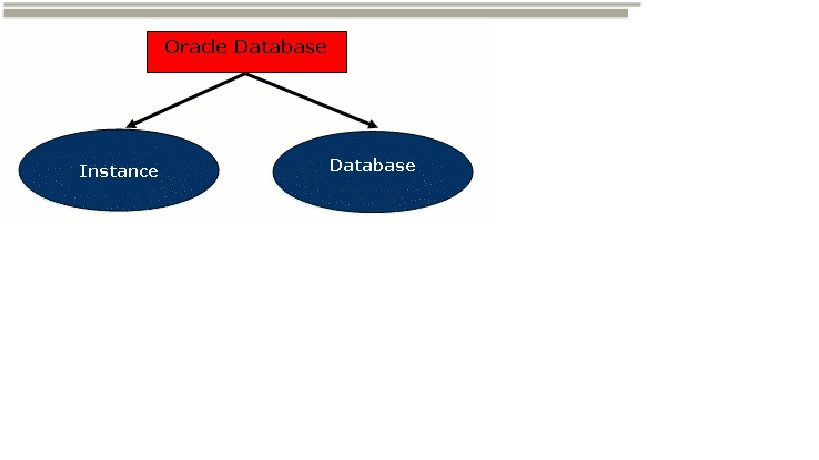
Basically, there are two main components of Oracle
database –– instance and database itself. An instance consists of some
memory structures and the background processes, whereas a database refers to
the disk resources. Figure 1 will show you the relationship. Figure 1. Two main components of Oracle database
Instance
As we cover above, the memory structures and
background processes constitute an instance. The memory structure itself
consists of System Global Area (SGA), Program Global Area (PGA), and an
optional area ––Software Area Code. In the
other hand, the mandatory background processes are Database Writer(DBWn),
Log Writer (LGWR), Checkpoint (CKPT), System Monitor (SMON), and Process
Monitor (PMON).And another optional background processes are Archiver (ARCn),
Recoverer (RECO), etc. Figure 2 will illustrate the relationship for those
components on an instance.
Figure 2. The
instance components
System Global Area
SGA is the primary memory structures. When Oracle DBAs talk about
memory, they usually mean theSGA. This area is broken into a few of part memory
–– Buffer Cache, Shared Pool, Redo Log Buffer, LargePool, and Java Pool.
Buffer Cache
Buffer cache is
used to stores the copies of data block that retrieved from datafiles. That is,
when userretrieves data from database, the data will be stored in buffer cache.
Its size can be manipulated viaDB_CACHE_SIZE parameter in init.ora
initialization parameter file.
Shared
Pool
Shared pool is
broken into two small part memories –– Library Cache and Dictionary Cache. The
librarycache is used to stores information about the commonly used SQL and
PL/SQL statements; and ismanaged by a Least
Recently Used (LRU) algorithm. It is also enables the sharing those statemens
amongusers. In the other hand, dictionary cache is used to stores
information about object definitions in thedatabase, such as columns, tables,
indexes, users, privileges, etc.The shared pool size can be set via
SHARED_POOL_SIZE parameter in init.ora initialization parameter file.
Redo Log Buffer
Each DML statement (insert, update, and delete) executed by users will
generates the redo entry. What isa redo entry? It is an information about all data changes made by users.
That redo entry is stored in redolog buffer
before it is written into the redo log files. To manipulate the size of redo
log buffer, you can usethe LOG_BUFFER parameter in init.ora
initialization parameter file.
Large
Pool
Large pool is an
optional area of memory in the SGA. It is used to relieves the burden place on
the sharedpool. It is also used for I/O processes. The large pool size can be
set by LARGE_POOL_SIZE parameter ininit.ora initialization parameter file.
Java
Pool
As its name, Java pool is used to services parsing of the Java commands.
Its size can be set byJAVA_POOL_SIZE parameter in init.ora initialization parameter file.
Program Global Area
Although the result
of SQL statemen parsing is stored in library cache, but the value of binding
variablewill be stored in PGA. Why? Because it must be private or not be shared
among users. The PGA is alsoused for sort area.
Software Area Code
Software area code
is a location in memory where the Oracle application software resides.
Oracle Background
Processes
Oracle background
processes is the processes behind the scene that work together with the
memories.
DBWn
Database writer
(DBWn) process is used to write data from buffer cache into the datafiles.
Historically, thedatabase writer is named DBWR. But since some of Oracle
version allows us to have more than onedatabase
writer, the name is changed to DBWn, where n value is a number 0 to 9.
LGWR
Log writer (LGWR)
process is similar to DBWn. It writes the redo entries from redo log buffer
into the redolog files.
CKPT
Checkpoint (CKPT)
is a process to give a signal to DBWn to writes data in the buffer cache into
datafiles. Itwill also updates datafiles and control files header when log file
switch occurs.
SMON
System Monitor
(SMON) process is used to recover the system crach or instance failure by
applying theentries in the redo log files to the datafiles.
PMON
Process Monitor
(PMON) process is used to clean up work after failed processes by rolling back
thetransactions and releasing other resources.
Database
The database refers
to disk resources, and is broken into two main structures –– Logical structures
andPhysical structures.
Logical Structures
Oracle database is
divided into smaller logical units to manage, store, and retrieve data
effeciently. Thelogical units are tablespace, segment, extent, and data block.
Figure 3 will illustrate the relationshipsbetween
those units.

good one its helpful for us..!
ReplyDeleteHELLO RAFFEEK, WE WANT ALL OS COMMANDS , CAN YOU UPLOAD THAT..!
ReplyDeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteIt's very useful for all.